Have you just come across the term ‘Anteverted uterus‘ on your clinical test reports and wondering what it implies? Could it be a serious condition that needs treatment? What causes it and how does it affect your life? While it does sound alarming, is it something to worry about?
Read on to find out all that you have wanted to know about Anteverted Uterus.
Table of Contents
What Is Anteverted Uterus?
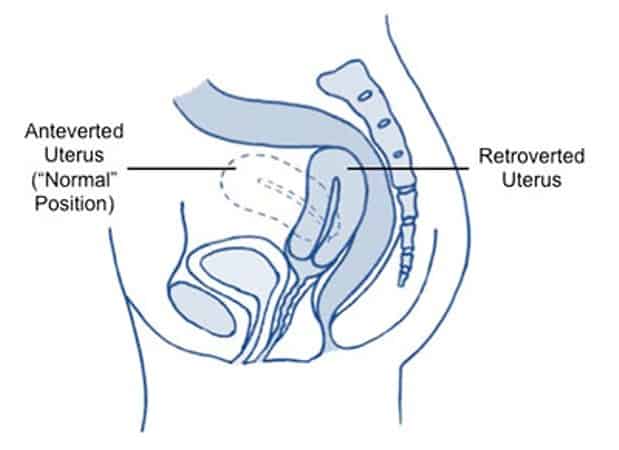
Anteverted Uterus is a term used to describe the tilt of the uterus. The position of the uterus is indicated by its tilt and the location of the fundus.
While a vertical uterus indicates mid-position and no tilt, an anteverted uterus is tilted forwards towards the abdomen, over the bladder.
Another related term is retroverted uterus, which means the uterus is tilted back towards the spine.
The top of the uterus, called the fundus also determines the position of the uterus. Anteflexed implies that the top of the uterus is forward like a C, while retroflexed means that the top is backward.
Anteverted uterus is the most common position of the uterus and is found in approximately 50 percent of women. However, the degree of tilt varies across individuals.
To understand this condition better, let us take a quick look at the uterus and its structure.
The Uterus At A Glance
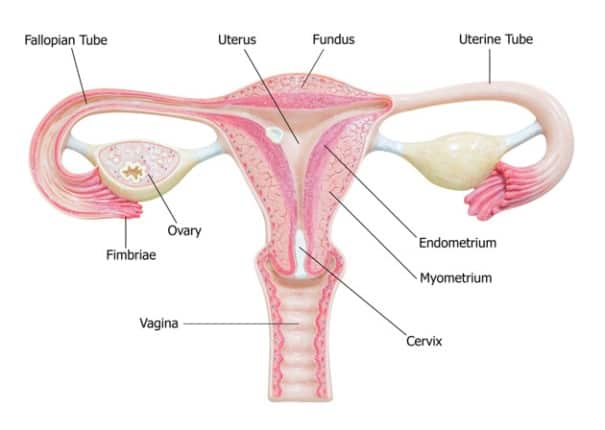
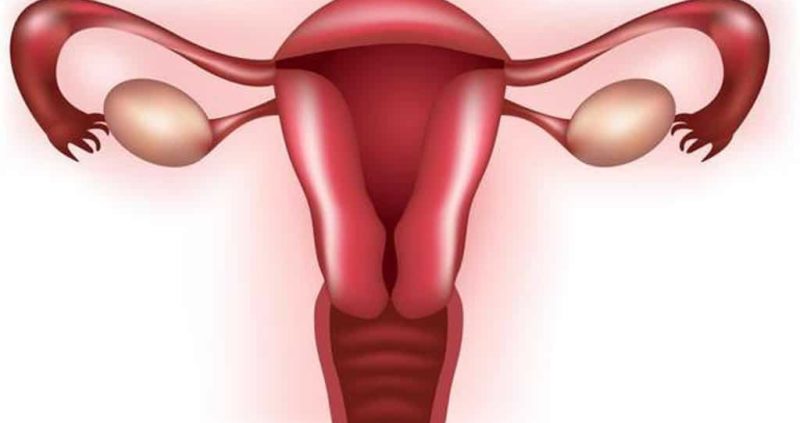
The uterus is a female reproductive organ and is pear-shaped with thick muscular walls. The uterus, also known as the womb, is where the baby is housed during gestation.
Situated between the rectum and the urinary bladder, in the pelvic region, it is around 8 cm long, 5 cm wide and 3 cm deep. The uterus of a healthy woman weighs about 60 grams.
The upper portion of the uterus is known as fundus, where the fertilized egg develops into a baby. The fundus is connected to the ovaries through the fallopian tubes. The lower part is called cervix, which leads to the vagina.
The fundus may be bigger in women who have delivered a baby, while it can be small during menopause, in women who have not had a delivery.
The inner layer of the uterus, called the endometrium, consists of blood vessels and mucous membranes. This lining thickens up during the menstrual cycle and is induced by hormones as a preparation for pregnancy. It is expelled from the body, in the absence of fertilization.
However, in the case of pregnancy, following fertilization, the lining is retained and the placenta forms to deliver nutrition and oxygen to the developing fetus.
The uterus and the cervix are attached to the sidewalls of the pelvis by ligaments. These flexible ligaments allow forward and backward tilting of the uterus. The normal position of the uterus is straight up and vertical.
The ligaments would be more flexible in women who have had vaginal deliveries, as compared to those who have not given birth.
Anteverted Uterus- Is It A Cause For Concern?
Doctors use the term anteverted to indicate the position of the uterus. Quite contrary to what many people think about this condition, it is not a cause of major concern.
This is a variation of the position of the uterus and does not affect its structure. The anteverted position of the uterus is generally not considered as a threat or abnormality, and it does not hinder reproduction.
Anteverted uterus has no specific impacts on the woman’s health. In fact, most women are not even aware of such a tilt.
In case of an anteverted uterus, the ovaries are at a higher position in the pelvis. Hence, it is less likely to be hurt during intercourse.
Anteverted uterus does not lead to abnormal pains or discomforts during menstruation.
The severity of the tilt and the degree of inclination vary with people and could determine the impacts of this condition. While small differences in orientation do not have any adverse effects, extreme tilting could hinder fertilization, thereby making it difficult to conceive.
Extreme cases of forward tilting may cause some discomfort during urination, due to pressure on the bladder.
How Does Anteverted Uterus Affect Fertility And Pregnancy?

Anteverted uterus does not usually affect fertility or sexual health of women. The condition does not have any adverse effects on the ability to conceive and bear children.
This is because the passage of sperms through the uterus and the process of fertilization are unaffected by the orientation or tilting of the uterus. Factors that affect this process include cervical mucus consistency and mobility of sperms.
Anteverted uterus is examined as a cause of infertility, only after other causes have been thoroughly considered and ruled out. Problems that may hinder conception include fibroids in the uterus, ovarian cysts, and scar tissues, which have no association with anteverted uterus.
This orientation does not interfere with any of the stages of pregnancy, right from the conception to giving birth. Anteverted uterus does not harm the health and development of the baby, nor does it put you at risk of a miscarriage.
While there are no complications caused by anteverted uterus during pregnancy, it would be safer to conduct regular checkups and visits to the doctor, to monitor any problems related to the positioning.
Why Does The Uterus Tilt Forward?
Factors that lead to anteverted uterus include body structure, pregnancy and childbirth, surgery, fibroid tumors, diseases in the pelvic region, and aging.
Body type and anatomy could be factors that cause tilting of the uterus. Changes in the body, occurring around the uterus may lead to change in orientation.
Availability of a lot of space in the pelvis or the friction and pressure of organs on each other may cause the tilt. Pressure from the urinary bladder could be a cause of anteverted uterus.
A person’s lifestyle, inclusive of sex does not change the orientation of the uterus.
Some women have been found to have anteverted uterus since birth, while others develop the condition, as they grow old. Normal growth and development may also lead to tilting of a uterus in mid-position.
Pregnancy or childbirth can also result in the uterus tilting toward the abdomen, from it’s the vertical position.
During pregnancy, the uterus expands in accordance with the child’s growth. Factors like pressure exerted and position of the child, along with the stretching of the uterus can cause the tilt.
The ligaments that keep the uterus in place, can be weakened and loosen up during pregnancy and delivery. This can lead to the change in position or tilting of the uterus.
These ligaments also become weak with progressing age and lose their ability to hold the uterus in place, thereby causing forward tilting. This increases the chances of anteverted uterus in women as they grow old than when they were young.
In most cases, the uterus returns to the normal mid-position after complete healing following childbirth. However, sometimes the changed orientation is retained.
Does Anteverted Uterus Affect Menstruation?
While a retroverted uterus has been found to cause abnormal pain during menstruation, an anteverted uterus does not cause such problems.
The forward tilting of the uterus is very common in women, and this does not affect the menstrual cycle.
Anteverted uterus usually does not cause any additional discomforts during menstruation or intercourse.
Individuals who find it painful or experience discomforts during menstruation should seek a doctor’s help. It is highly likely that these are caused by some other condition and is not associated with the forward tilting.
Can The Anteverted Uterus Change Position?
Factors such as pressure exerted and weight gain may lead to repositioning of the uterus. This, however, does not affect overall health or the ability to conceive again. As discussed earlier, the change in position of the uterus may happen after childbirth.
Severe injury, trauma or accidents can change the orientation of the uterus.
If the anteverted position changes to a retroverted one, where the uterus tilts backward, it may indicate problems including pelvic inflammatory disease or endometriosis.
Treatment For Anteverted Uterus
As we have seen, there are no problems or complications associated with anteverted uterus. It does not interfere with conception, pregnancy or childbirth. Hence, it does not require any treatment.
It is extremely rare that you would experience discomforts that are caused by anteverted uterus.
If you do experience any pain or discomfort during intercourse, pregnancy or menstruation, do not hesitate to consult your doctor. They would diagnose the underlying cause and advise appropriate treatment.
What Else Could Help?
Here are a few non-invasive ways to improve overall reproductive health. In case you have any complications or specific conditions, it would be better to seek approval from your doctor before you practice these.
1. Contraction And Relaxation Of The Pelvis
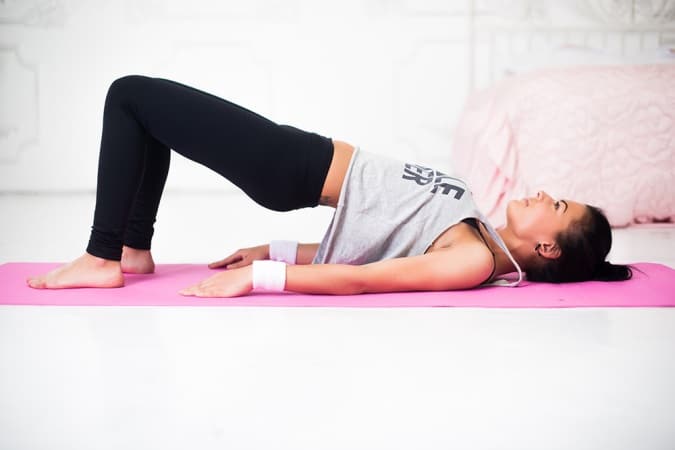

Lie flat on your back, with the arms on the sides. Taking a deep breath, slowly lift the buttocks to an inch above the ground. After retaining this position for five seconds, slowly exhale and release the position. You can repeat this five times.
2. Knee Chest Exercise
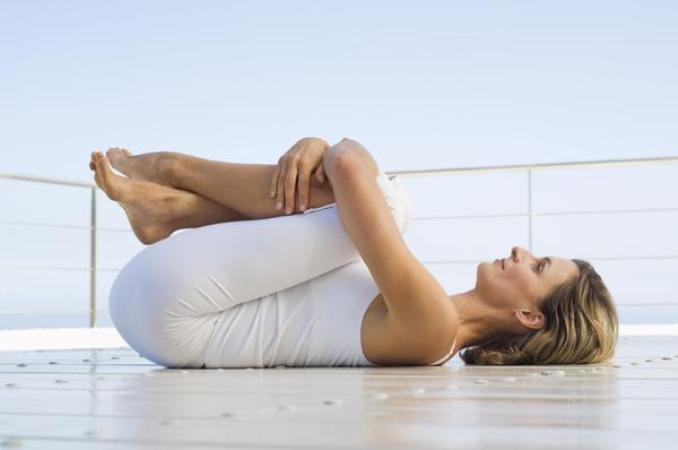

Lie flat on the ground with the knees bent and feet placed flat on the floor. Lift one knee up to the chest, and then hold it with both hands, keeping this position for 15 seconds before releasing.
Repeat the same with the other knee. Now, do this exercise four times with each knee, alternating between the two.
3. Yoga

You can also consider doing yoga, specifically poses that help to strengthen the abdomen and pelvic muscles. These help to relax, balance hormones and increase blood supply. Some of these also help in improving fertility.
4. Self Fertility Massage
Self Fertility Massage comprises of massage techniques that focus on the pelvis and the lower abdomen to help improve the functioning of the uterus and balance the menstrual cycle. These can boost reproductive health and fertility.
The techniques improve blood circulation to the uterus and cleanse it. It balances the hormone cycles and strengthens the uterine muscles.
In short, the term anteverted uterus just characterizes the orientation of the uterus, differentiating it among other types of positions.
It is one of the most common orientations found in women, not known to cause any health issues and is considered to be normal.