The Sternal Angle helps in locating various other important parts and structures.
Let’s read more about it in this article.
Table of Contents
The Sternal Angle
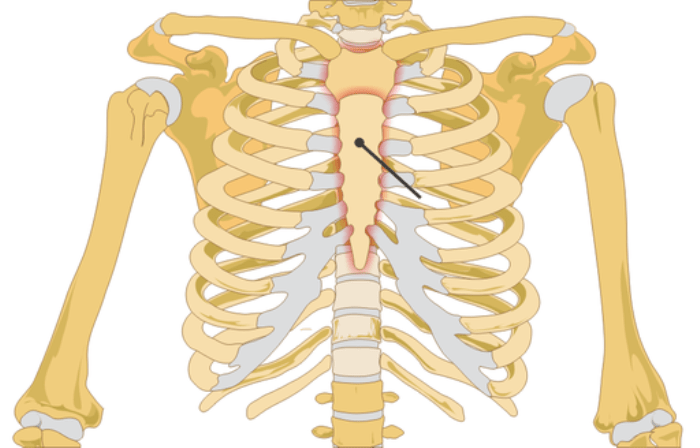
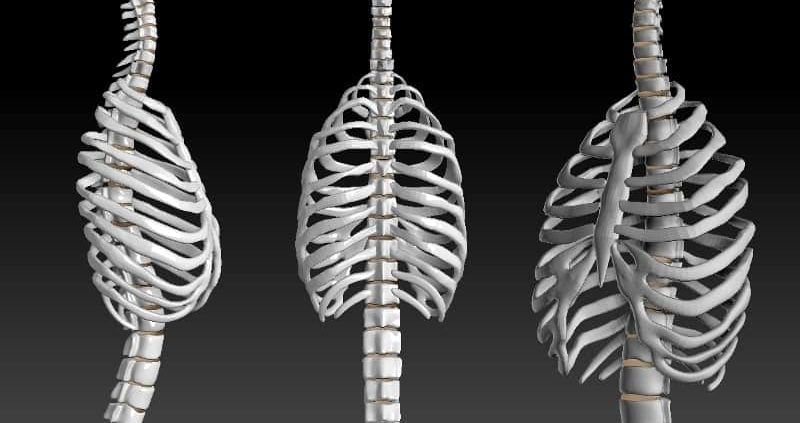
The Sternal Angle is the joint formed between the Manubrium .i.e. the head of the sternum and the body of the sternum.
The Sternum or the Breast Bone is a long flat bone located in the center of our chest, shaped like a necktie, that joins the right and the left ribs by cartilages to form the rib cage.
Since it forms the center of the rib cage, it helps to protect internal organs like the heart and lungs along with several blood vessels and nerves from any damage or injury.
Imagine the Sternum to look like a necktie.
The top, triangular part is the Manubrium, and the long flat part is the body of the sternum, ending at a small point called the Xiphoid Process.
The Sternal Angle is then the joint that is formed between the Manubrium and the body of the sternum.
The Sternal Angle is also known as Angle of Louis after Pierre Charles Alexandre Louis, a French physician, or Manubriosternal Junction.
Location Of Sternal Angle
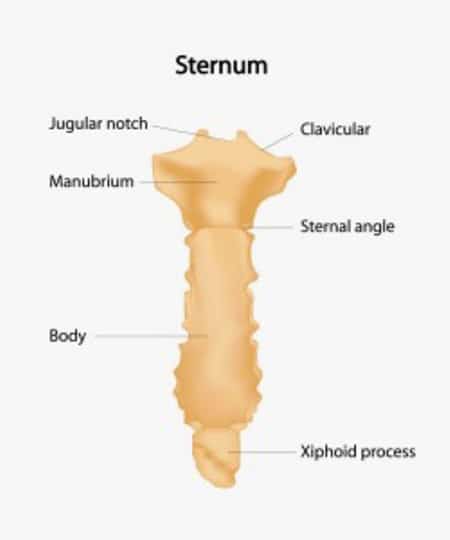
The Sternal Angle is located between the collar bones, at the base of the neck, about 5 centimeters down the bony ridge of the sternum, below the suprasternal notch.
The suprasternal notch is the dip between the neck and the collar bones. The Sternal Angle is located roughly around the second pair of ribs.
Significance Of The Sternal Angle
The Sternal Angle is a very important marking point in the human body because it helps in locating various other important parts and structures.
Being centrally located in the chest area and covering most of the internal organs, the Sternal Angle has several important structures that lie behind it, and it helps physicians and doctors locate those structures in time for treatment.
To remember the structures whose location can be marked by the Sternal Angle, remember the word RATPLANT, where each alphabet stands for the structure that is marked.
a. R For Ribs
The Sternal Angle lies roughly around the second pair of ribs in the rib cage and is the point from which the ribs can be counted. It also marks the location of the second pair of costal cartilages that join the second pair of ribs to the sternum.
It also marks the location and level of the intervertebral discs, which lies between thoracic vertebra T4 and T5, and plays a major role in shock absorption for the spine.
b. A For Arch Of The Aorta
The Aorta is one of the major arteries of the heart that supplies blood to the lower half of the body. The Aorta starts from the heart, forms an arch and then runs downwards towards the lower half of the body.
The beginning and end point of the arch of the Aorta is located roughly behind the Sternal Angle and is hence easy to locate.
c. T For Trachea
The Trachea or the windpipe is the muscular tube that connects the nose to the lungs. The trachea starts as a single tube from the nose and then divides into two branches known as the primary bronchi while entering the lungs.
The point at which the Trachea divides into two to enter the lungs is located by the Sternal Angle as it divides at about the same level as the Sternal Angle.
d. P For Pulmonary Trunk Bifurcation
The Pulmonary Trunk is one of the main arteries of the heart that carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
Before entering the lungs, the Pulmonary Trunk bifurcates or divides into the right and left pulmonary artery and then enters the corresponding lung.
The point at which the Pulmonary Trunk divides before entering the lungs lies at about the same level as the Sternal Angle and is used by doctors to locate that point.
e. L For Left Recurrent Laryngeal
The Left Recurrent Laryngeal is a branch of the vagus nerve, the tenth cranial nerve, that is responsible for controlling the functioning of the intrinsic muscles of the larynx or the voicebox.
The vagus nerve controls the involuntary functions of the heart and the digestive system like the heart rate, intestinal peristalsis, sweating, gag reflex, etc.
The point at which the Left Recurrent Laryngeal loops under the aorta and the vagus nerve comes down is located behind the Sternal Angle at around the same level.
LigamentumArteriosum
The LigamentumArteriosum is a small ligament that connects the arch of the aorta to the pulmonary trunk. This ligament can be located by the Sternal Angle.
f. A For Azygos Vein
The Azygos Vein is a vein that is located on the side of the thoracic vertebral column. Draining itself into the superior vena cava.
It connects the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava, two arteries of the heart, and thus provides an alternative path for the blood to the right atrium of the heart when either of the venae cavae is blocked.
The point at which the Azygos Vein drains itself into the superior vena cava is located at roughly the same level as the Sternal Angle.
g. N For Nerves
The cardiac plexus or the nerves present at the base of the heart are located at around the same level as the Sternal Angle.
i. T For Thoracic Duct
The Thoracic Duct, which carries water and solutes from the lymphatic system, drains into the left subclavian vein at a point that can be located on the level of the Sternal Angle.
The Thoracic duct travels from the right side to the left side of the body from behind the esophagus at this point.
Though this point is located a little above the Sternal Angle, the location of the Sternal Angle proves useful in finding the point.
The Sternal Angle Also Has The Following Functions
- Forms the boundary between the superior and inferior mediastinum of the thorax .i.e. the median region of the thorax. The median region of the thorax is the space between the lungs and the plane of the Sternal Angle is used to divide it into the fore mentioned regions.
- Is the point at which the sternum moves forward and backward during respiration.
- It is the highest point of the pericardial sac, i.e., the muscular sac that covers the heart and its blood vessels.
Issues Related To The Sternal Angle
Since the Sternal Angle is part of the sternum, a bone that forms the center of the rib cage, it is prone to several injuries and damages due to the sternums protective functioning.
Some of the issues related to the Sternal Angle are:
i. If the location of the Sternal Angle is different due to developmental issues in a person, it can lead to several complications like:
ii. Inaccurate or improper counting and numbering of ribs
iii. Issues in locating several of the body structures mentioned previously
iv. The complication in the movement and structure of the sternum
v. Playing sports like football, basketball, weight lifting, etc. may often lead to injuries to the sternum and cause pain on the Sternal Angle
vi. Motor vehicular accidents like a car crash or getting slammed against the steering wheel of a car can cause injuries to the rib cage and the Sternal Angle.
vii. Hitting, punching or any other form of a direct physical assault aimed at the chest area can also injure the Sternal Angle.
viii. Respiratory diseases like tuberculosis and syphilis can cause a strain on the Sternal Angle
ix. Conditions such as Costochondritis, which is an inflammation of the rib cartilages, can make the area around the Sternal Angle feel tender and painful with the pain ranging from mild to severe.
Treatments For Sternal Angle

Since most of the issues related to the Sternal Angle are physical, they can easily be treated by a qualified doctor.
Some of the treatments and precautions to avoid injuries to the Sternal Angle are:
1. If your Sternal Angle is located at a different point than what is normal .i.e. near the second rib, it is best to consult a doctor and have an x-ray done for future reference incase of an emergency or treatment.
2. While playing sports or lifting weight be careful to avoid any injury or direct strain on your sternum and chest area as it may lead to issues and pain in the Sternal Angle region.
3. Always wear a seat belt while driving and try and ensure that your vehicle has safety features like airbags in them. Not only will they save your life in case of an accident but also protect you from injuries to your chest area and rib and sternum fractures.
4. Avoid physical conflict that may result in damage to your ribs and chest.
5. Early treatment of diseases like tuberculosis and syphilis will help in a speedy recovery from the disease and also avoid any pain and inflammation at the Sternal Angle due to the labored movement of the sternum while breathing.
6. In the case of inflammation or pain in the Sternal Angle region, apply a hot water bottle or a heat pack to decrease the inflammation and relieve the cartilages and muscles.
7. If you suffer from continuous pain or discomfort in the Sternal Angle region, consult a doctor for possible diagnosis and remedies to cure it.
The Sternal Angle forms a major marking point in the human body and is widely used by doctors and physicians for locating several body structures.
On it own, since the Sternal Angle forms the joint of the sternum it is important to avoid any injury or inflammation to it since it can cause problems in breathing and chest pains.
Avoiding direct strain and injury to the chest and ribs and overall maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help in keeping the Sternal Angle function smoothly and stay free of issues and injuries.